Electric vehicles and charging stations
Fire safety solutions for places used for charging electric vehicles in enclosed garages
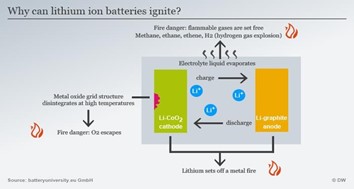
Lithium-ion batteries - sources of fire
Causes:
- Accident or collision causing mechanical damage to the battery. Sometimes, the fire re-ignites hours or days after the accident (Silicon Valley, Tesla car accident).
- Short-circuiting of the battery due to overheating caused by improper charging, overcharging, or the battery's condition, as well as design flaws.
Progression of the reaction known as thermal runaway:
A lithium-ion battery consists of a cathode [LiCoO2], a graphite anode, and electrolytes [ethylene carbonate/ethyl methyl carbonate (EC/EMC)].
The products of the thermal runaway reaction are:
- CO2,
- CO,
- H2, highly flammable,
- CH4, highly flammable methane,
- C2H6, extremely flammable ethane,
- C2H4, flammable ethene,
- O2 (oxygen)
Fire extinguishing agents
Ineffective:
- Any foam extinguishing agents - the thermal runaway reaction produces oxygen and flammable gases, and foam typically works by cutting off the oxygen supply. In this case, foam is not effective.
- Additionally, foam is much less efficient at cooling compared to water streams. This was confirmed in an NTSB study, which found that foam is not suitable for extinguishing batteries in electric vehicles. See the attached photos.
- Foam is suitable for effectively extinguishing interior fires, but through firefighting personnel and water streams in the case of gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Fixed foam-based fire suppression systems are not applicable and would also cool the garage structure less effectively against the destructive action of flames compared to water streams.
- There is also no standard on which to base the design of a fixed foam-based fire suppression system for charging stations in garages
Recommendations from RSA (a British insurer with a 300-year history):
For Permanent Water Sprinkler Systems designed in accordance with globally recognized standards:
Standard Requirements for Garages:
- LPC (Loss Prevention Certification Board): Ordinary Hazard 2 – 5 mm/min over 144 m² (180 m² for dry systems).
- NFPA (National Fire Protection Association): Ordinary Hazard 1 – 4.1 mm/min over 370 m² (480 m² for dry systems) to 6.1 mm/min over 260 m² (338 m² for dry systems).
- FM (Factory Mutual): Hazard Category 2: 8 mm/min over 230 m² (300 m² for dry systems).
RSA's Recommended Elevated Requirements Due to Charging Stations and the Increasing Use of Plastic in Vehicle Construction (average 200 kg in 2014 vs. 350 kg in 2020):
- LPC: High Hazard Process 1 (HHP1): 7.5 mm/min over 260 m² (350 m² for dry systems).
- NFPA: Extra Hazard Group 1 (EH1): 8.2 mm/min over 465 m² (605 m² for dry systems) to 12.2 mm/min over 230 m² (300 m² for dry systems).
- FM: Hazard Category 2: 8 mm/min over 230 m² (300 m² for dry systems).
Fire extinguishing agents for extinguishing electric vehicle fires
| Lokation | Fire Protection and Safety | Risk level |
|---|---|---|
| Underground |
|
|
| Public Outdoor Area |
| |
| Inside the Building (Ground Floor and Above)
|
| |
| Top Floor |
|
Recommendations - Fire Protection Association, RC59: Recommendations for fire safety when charging electric vehicles, 2021:
Benefits of sprinkler system installations for protecting underground garages and charging stations
Advantages of sprinkler system installations for protecting underground garages and charging stations:
-
Effective Structure Protection
-
Smoke Reduction
-
Fire Control
-
Low Installation and Maintenance Costs
-
Safety from Electrical Hazards
-
Evacuation Support
-
Recommended by Insurers
-
Availability of Qualified Installers and Servicers
Additionally, RSA recommends maintaining a minimum distance of at least 5 meters between the charging or landing area and other vehicles, further enhancing safety in these areas.
Conclusion - Recommendations
Closed garage spaces equipped with electric vehicle charging stations should be equipped with:
- An automatic sprinkler fire suppression system designed and installed in accordance with NFPA and/or FM standards with elevated water spray density requirements.
- Adequate firewater drainage with appropriate capacity.
- A minimum distance of at least 5 meters between charging stations and parking spaces for other vehicles in the garage.
- Provision for fire ventilation.
- Placement of charging stations as close as possible to garage entrances/exits.
- Availability of above-ground hydrants in the vicinity with a flow rate of at least 30 liters per second for continuous battery cooling by the fire brigade, connected from below the water curtains.
- Unobstructed access for the Fire Department to conduct firefighting operations.
- A minimum gap of at least 2 meters between vehicles in the charging area to facilitate free access for the Fire Department and effective fire control by the sprinkler system.


